We will go over the essential elements a fee management system must have, its high-level, low-level design and database design. We will also look at some of the features that turnkey software solutions offer.
Table of contents:
- Fee Management System
- System Requirements
- Functional Requirements
- Non - Functional Requirements
- Software Requirements
- High-Level Design
- For a small setting
- For a large setting
- Low-Level Design and Classes
- Database Design of Fee Management System
- Turnkey Software Solutions
Fee Management System
A fee management software is a software that automates the collection of fees and generation of receipts. For example in a school environment, the system manages tuition fees, miscellaneous fees, project fees and other charges for student services. It helps the school administrator to automate the fee collection, generate receipts, refunds and invoice reminders. It increases efficiency and reduces the cost needed for maintaining manual records and saves time and effort for both the user and the school administrator.
System Requirements
The key requirements that need to be offered by the fee management system can be classified into functional and non-functional requirements.
Functional Requirements
- Allow the school administrator to add and remove new students.
- Allow the school administrator to add and manage the subjects and the associated fees.
- Users can retrieve invoice and make payment.
- The system should notify the user and school administrator about the overdue invoices.
A more detailed list of key features that need to be supported by the system is given in the use case diagram.
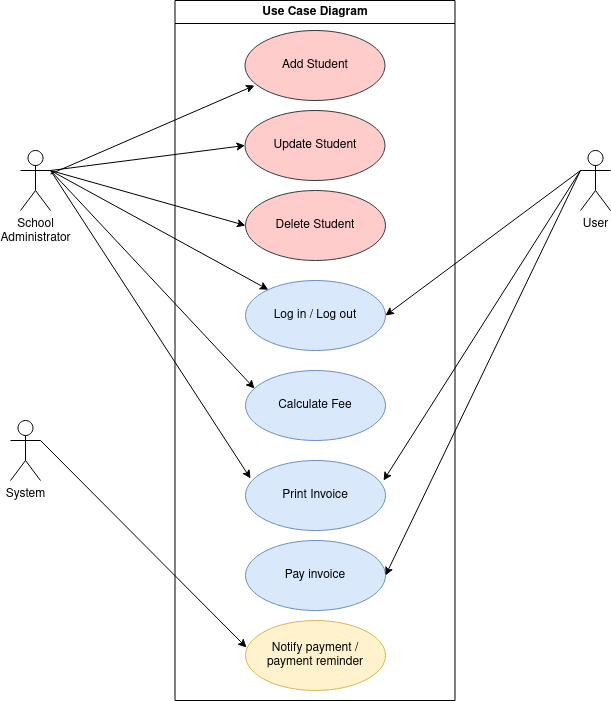
There are 3 actors in the use case diagram. The User, the School Administrator and the System.
User - The user can log in, make payment for the invoice, print a copy of the invoice for their records.
School Administrator - The School Administrator registers new student account, calculate the fees payable and print out the invoices to issue to the students.
System - The system is the fee management system itself. It keeps track of the invoices and sends notifications to the user and school administrator about the overdue invoices.
Non - Functional Requirements
Usability
Usability is the main non-functional requirement for a fee management system. Everyone should be able to understand the user interface (UI) and obtain the necessary information without the need for any specialized training. Different languages can be provided based on the requirements.
Accuracy
Accuracy is another important non-functional requirement for the fee management system. The fees calculated should be correct, consistent, and reliable.
Availability
The System should be available at least during the academic year and must be recovered within an hour if it fails. The system should respond to the requests within two seconds.
Maintainability
The software should be easily maintainable, with adding new features and making changes as simple as possible.
Software Requirements
- A server running Windows Server/Linux OS
- A backend language such as like Java, Python to do the computation of the fees
- Front-end frameworks like Angular/React/Vue for the user interface.
- Relational DBMS such as MySQL, PostgreSQL.
- Containers and orchestration services like Kubernetes (for a large setting such as a University).
High Level Design
For a Small Setting (School):
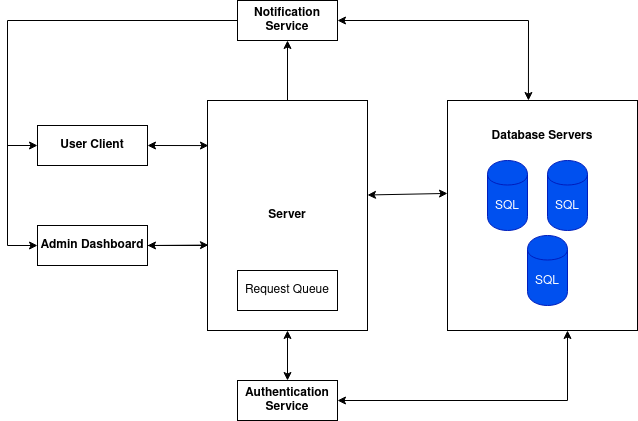
In a school environment, the users are the students. The traffic is usually low with an estimated 1,000 concurrent users at the peak. A group of servers each with 16GB of RAM and a capable processor should be able to handle the load. Each server may need to handle several requests at a time. The requests can be queued and a reply can be sent to the user while the request is being processed.
The user can access the system through a client site or app with a registered account. The school administrator can access the admin dashboard and interface using the admin account.
Handling the authentication is done by a separate service. The authentication service has direct access to the accounts on the database. The notification service checks the database for any overdue invoices and alerts the user and the school administrator.
Data such as user accounts and fees information is primarily relational. We can use a relational database like MySQL to store them. For backup and availability, the database servers can be configured in a master-slave arrangement.
For a Large Setting (University):
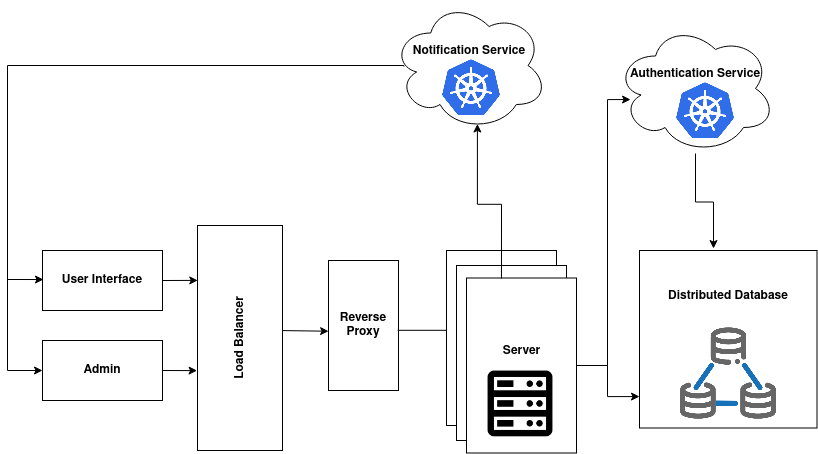
For some Universities, the number of concurrent users can get up to 10,000 and above at its peak. These systems can also have separate user and admin interfaces for students from different faculty.
The servers may be distributed across different regions in the country with load balancers to distribute the traffic. Reverse proxy servers may be deploy for web acceleration using techniques such as compression, SSL termination and caching request. Services such as authentication and notification may be deployed as separate containers. This makes scalability considerably easier and makes it simpler to add new services.
We can adopt distributed database approach to spread the database across different campus locations. The data is located at the campus where it is most frequently accessed, yet each authorized user has access to the whole database.
Low-Level Design and Classes
Let’s examine the various classes and functions associated with the fee management system in order to get a better understanding of the system.
class Person:
def __init__(
self,
first_name: str,
last_name: str,
gender: str,
address: str,
phone: int
):
class Student(Person):
def __init__(
self,
userid: str,
email: str,
password: str):
def login(self, email: str, password: str):
def logout(self):
def payInvoice(self, invoice_id: int):
class Administrator(Person):
def __init__(
self,
userid: str,
email: str,
password: str):
def login(self, email: str, password: str):
def logout(self):
def createInvoice(self, student_id: int, amount: int):
The Person class is the base class and contains fields for the basic information such as name, address, etc. The Student class inherits the Person class and adds fields such as a unique user id, login email, password and functions to login and logout. Both the Student and Administrator classes inherit the Person class. The student can pay for the invoice and the school administrator can create invoices for the students.
Database Design in Fee Management System
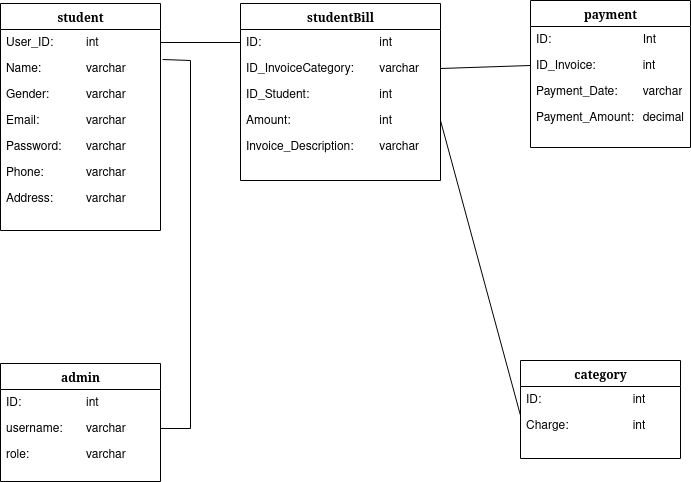
The above image shows one possible database schema for the fee management system.
The student table stores the user details such as a unique user id, name, contact, and login information. The admin table references the user id as a foreign key and stores the role of the admin such as Supervisor, Assistant, etc.
The studentBill table contains the information about the id of the Student, the amount payable, category of the fees and a brief description of the invoice. The category table stores the charges corresponding to the invoice category. The payment table stores the amount paid and when the payment was made.
Turnkey Software Solutions
Below are some of the turnkey software solutions available:
- SkoolBeep
- Edumarshal
- Camu
In general, the features provided by the turnkey software solutions include report generation facility such as fee receipts, fee payment reports that allow tracking of outstanding invoices. The software provide both automatic online and offline data backup facilities. In addition, the system is able to sync with payment gateways for a secure transaction. Real-time notification in the form of SMS, email, push notifications keep the students informed about fee dues and financial transactions.
This article was originally published at OpenGenus: